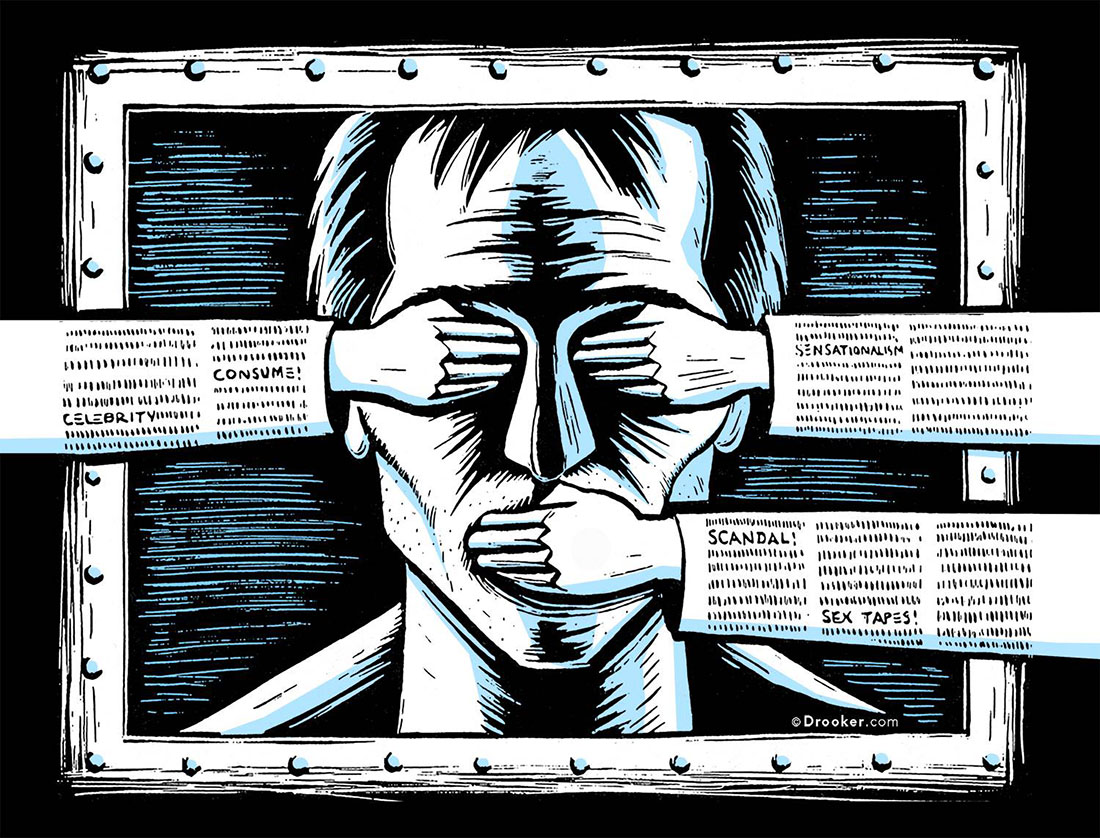
Don't use the word "war" and remove materials about the operation in Ukraine based on non-Ukrainian, official sources, Roskomnadzor, Russia's state media and Internet regulator, has ordered independent media outlets. Public and private censorship on the Internet works well. Is restricting freedom of speech always wrong?
What is Internet censorship?
What is censorship? Simply put: it is the control and restriction of information. We usually associate censorship with a state that prohibits the publication of facts that are inconvenient for the rulers.
However, more and more often, the heads of large technology platforms are accused of censorship: Google, Facebook, and Twitter.
Censorship in the media is a well-known phenomenon. Restrictions on freedom of expression and belief have reached a new level with the progressive digitization. Internet censorship has entered the scene. Not only political censorship and not only in China. Private online censorship, such as censorship of social media posts, is no less important.
Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; This right includes the freedom to hold opinions and to seek, receive and impart information and views through any media and regardless of frontiers, according to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
However, a beautiful declaration often remains an empty slogan. The Internet was supposed to be a place where everyone could freely express their thoughts and beliefs. However, this has not happened. Internet censorship works well. Advances in technology, such as artificial intelligence, are making it more and more effective at blocking content.

Internet censorship - what is it about?
What is Internet censorship? State censorship of the Internet is:
- technical restriction of access to the Internet (complete blocking of access or selected sites);
- penalties for using the services or websites, or distribution of specific content;
- creating barriers (e.g., legal or financial) that restrict access to the www;
- illegal activities, such as hacking into websites and/or removing content.
The state can censor information preventively (before publication) or after the fact (by punishing people who have published, for example, news critical of the government on the Internet). In practice, censorship on the Internet has many faces. It is usually used for the greater good, in particular:
- protection of the weak (for example, children in front of violent photos or videos);
- protection of victims (for example, avoid publishing images of victims of crime or tragic events);
- ensuring safety state or system (e.g., censorship imposed by the Communist Party of China);
- compliance with the rules adopted by the owners of large social networks such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter (for example, blocking the account of US President Donald Trump).
We can also easily find examples of actions that border on censorship. For example, IT departments block access to certain websites on employees' work computers. Parents have a choice. countless programs that can be installed on children's smartphones and block certain websites (Internet censorship in schools and at home).
Let's see what kind of materials are censored online and why.

What material is censored on the Internet?
The most censored materials on the Internet include:
- violenceFor example, photos and films of military operations and riots;
- pornographyFor example, posting photos/videos with erotic content on YouTube;
- fake news - any type of content that contains lies and manipulative messages;
- hate speech, For example, racist posts and content shared on social media;
- materials criticizing the actions of the authorities, For example, showing the bombing of Ukrainian cities by the Russian army.
Which countries censor the Internet? State censorship on the Internet
Access to online content is mostly blocked in non-democratic and repressive countries. The list of countries with the most censorship was prepared in 2019 by the Committee to Protect Journalists:
- Eritrea
- North Korea
- Turkmenistan
- Saudi Arabia
- China
- Vietnam
- Iran
- Equatorial Guinea
- Belarus
- Cuba
Authorities in these countries use traditional methods (e.g., intimidation of journalists), but they also readily resort to digital censorship.

Threats of censorship on the Internet
What are the consequences of blocking content on the Internet? Are publishers being persecuted? The list of consequences includes:
- lack of user access to the full range of information;
- misleading them about political and economic events;
- violation of democratic principles (voters cannot vote fairly without full information);
- manipulation of public opinion by the rulers.
Consistently applied state censorship gives citizens a distorted view of the world. Many of them are beginning to see censorship as extremely positive. For example, 26 percent of Russians believe that media censorship is absolutely necessary.
Censorship of social networks and freedom of speech
Just a few years ago, it was states that most often censored the Internet. But increasingly, large digital companies such as Google, Facebook, and Twitter are being accused of censorship. The most high-profile example is the blocking of Donald Trump, the former US president, on Twitter.
Copyright and censorship
According to some non-governmental organizations and institutions, copyright issues can be a cover for censorship on the Internet. This includes, for example, filtering the Internet in search of pirated materials. This requirement is set by one of the European Union's directives (2019/790 on copyright and related rights in the digital single market).
Benefits of Internet censorship - when it can be justified
Sometimes Internet censorship is applauded by the majority of the public. This is one of those times. content that is a manifestation of psychological violence:
- creating fake accounts to ridicule or attack other people/groups/minorities;
- defaming other people on forums and social networks;
- use of profanity;
- using altered photos/videos that are intended to harm other people.
Fighting haters is not enough. Russia's attack on Ukraine brought examples of online censorship that many considered appropriate: blocking access to Russian propaganda websites (Sputnik, RT TV) and their Facebook pages, and removing mobile apps from the Google Play store. In this way, "noble" censorship limited the scope of disinformation practiced by Russia.